Exothermic reactions are chemical reactions in which heat is released. They are produced due to the energy of the molecules involved in the reaction. In this case, the energy of the product molecules is less than the energy of the reactant molecules.
When we speak about an exothermic reaction, we refer to a chemical reaction, which releases energy to the surroundings in the form of heat or light during its execution. When this phenomenon occurs, we can say that the reaction products have less energy than the reactants that created them.
Thermodynamically, we can say:
Exothermic reactions are those chemical reactions that have the particularity of releasing energy to the surroundings.
The flow of thermal energy that occurs in a chemical reaction that runs at constant pressure is measured by a magnitude known as enthalpy, the representation of the energy change between a thermodynamic system and its environment.
In different areas of study, such as engineering, the enthalpy variation of a chemical reaction is used to classify this reaction as exothermic or endothermic. This variation is expressed as:
ΔH
If its value is negative or less than zero, it indicates that we are facing an exothermic reaction. We can indicate it mathematically as follows:
ΔH < 0
Importance of exothermic reactions
Exothermic reactions are important for life since living organisms use this chemical reaction to obtain the energy they require to stay alive. This process is known in biochemistry as metabolism.
Oxidation reactions are usually exothermic. These reactions generate fire and occur with great speed and violence. This phenomenon is commonly known as combustion and it is very important in almost all industrial processes and the daily life of human beings.
Condensation is another example of the importance of exothermic reactions since it allows the recovery of elements in a gaseous state in liquids by releasing energy into the environment.
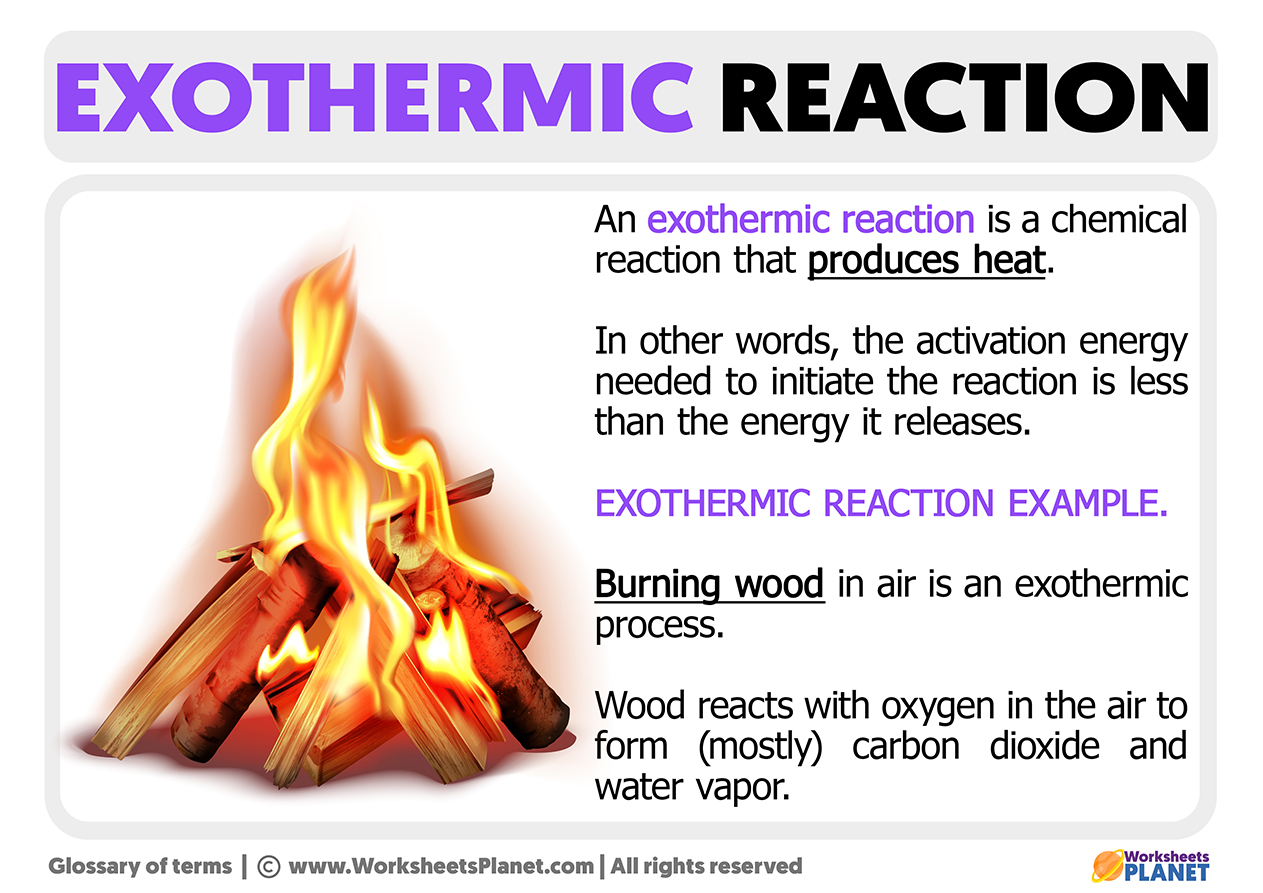
An Example of an Exothermic Reaction
Any combustion reaction, such as the one produced by coal or wood mixed with oxygen, generates carbon dioxide. These types of reactions not only release heat but also release light (fire).

