Hey Science Teachers! Here you have new resource for your class. This totally free material is made up of 9 different slides that will help you explaining what food chains are to your students. Appart from the theory slides, you’ll find a craft template. Your students will love it!!
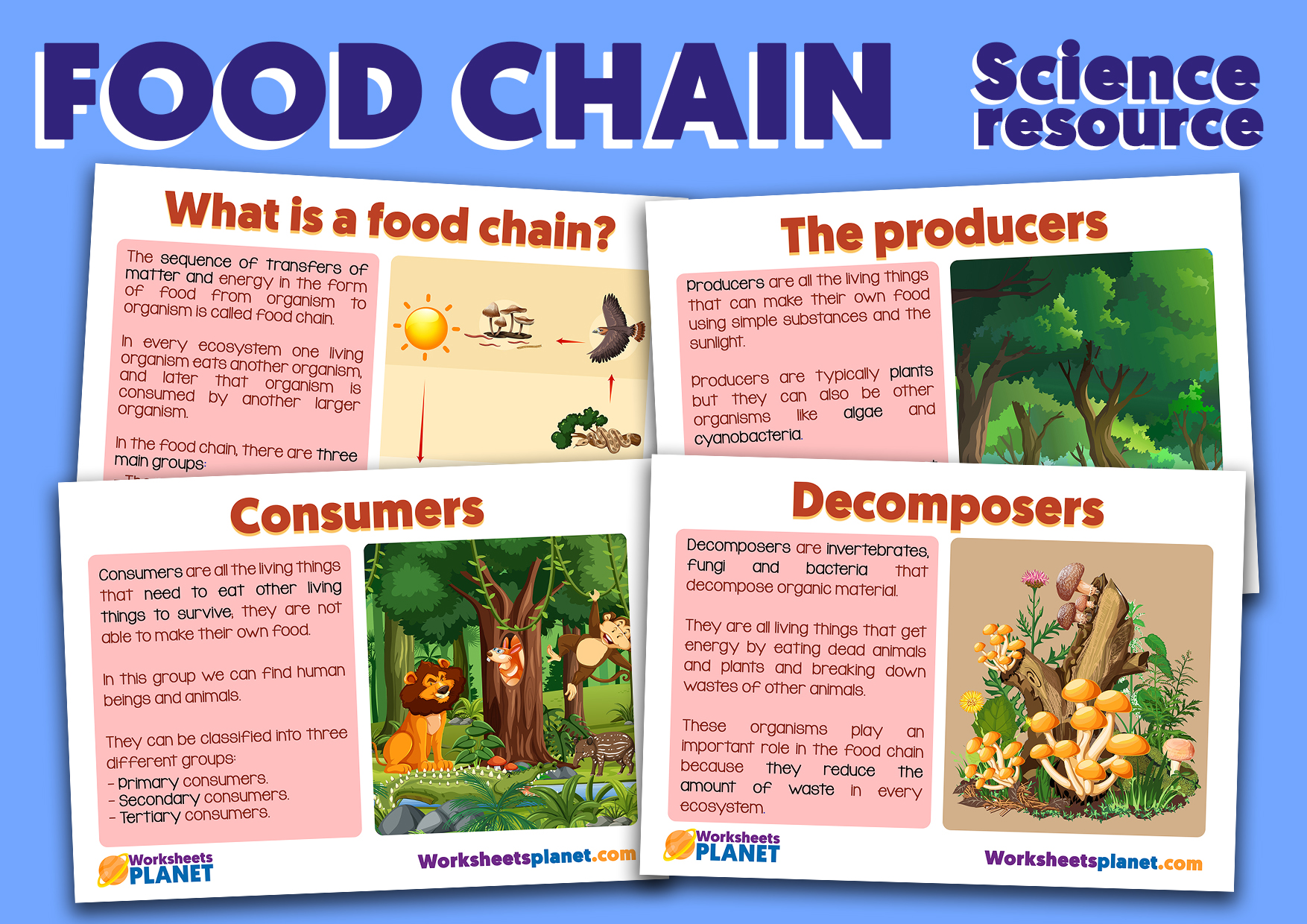
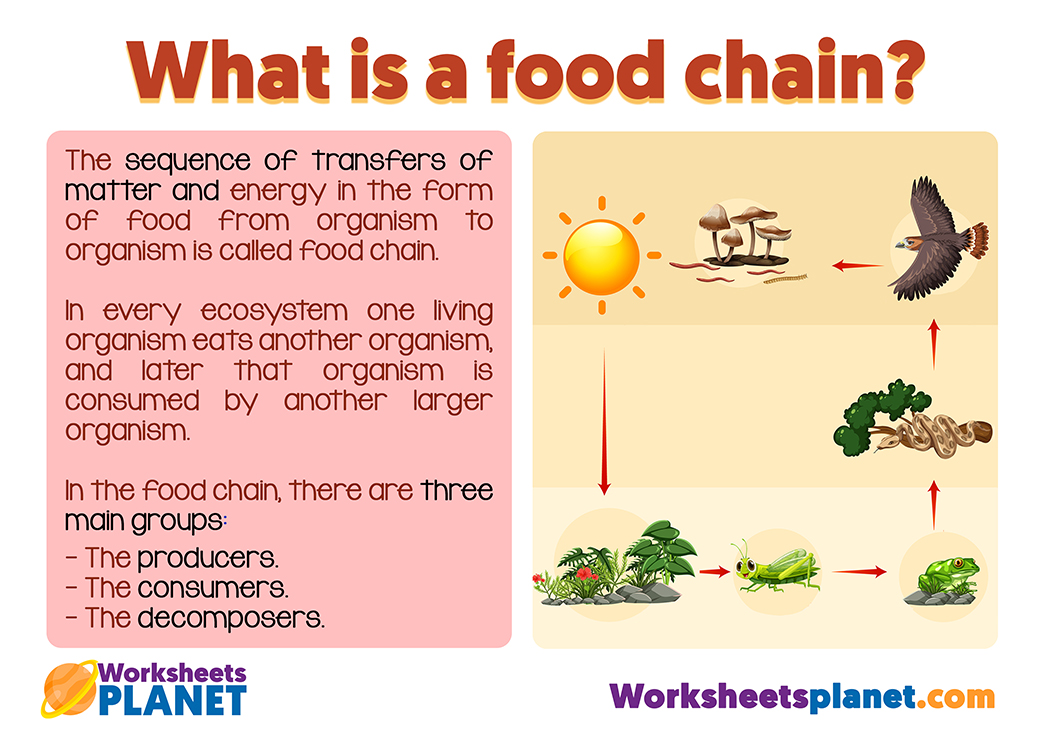
What is a food chain?
The sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism is called food chain. In every ecosystem one living organism eats another organism, and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism. In the food chain, there are three main groups:
- The producers.
- The consumers.
- The decomposers.
What are the producers in the food chain?
Producers are all the living things that can make their own food using simple substances and the sunlight. Producers are typically plants but they can also be other organisms like algae and cyanobacteria. Producers are the lowest trophic level in any food chain, what means they are the first ones in the survival process of every ecosystem.
What are the consumers in the food chain?
Consumers are all the living things that need to eat other living things to survive; they are not able to make their own food. In this group we can find human beings and animals. They can be classified into three different groups:
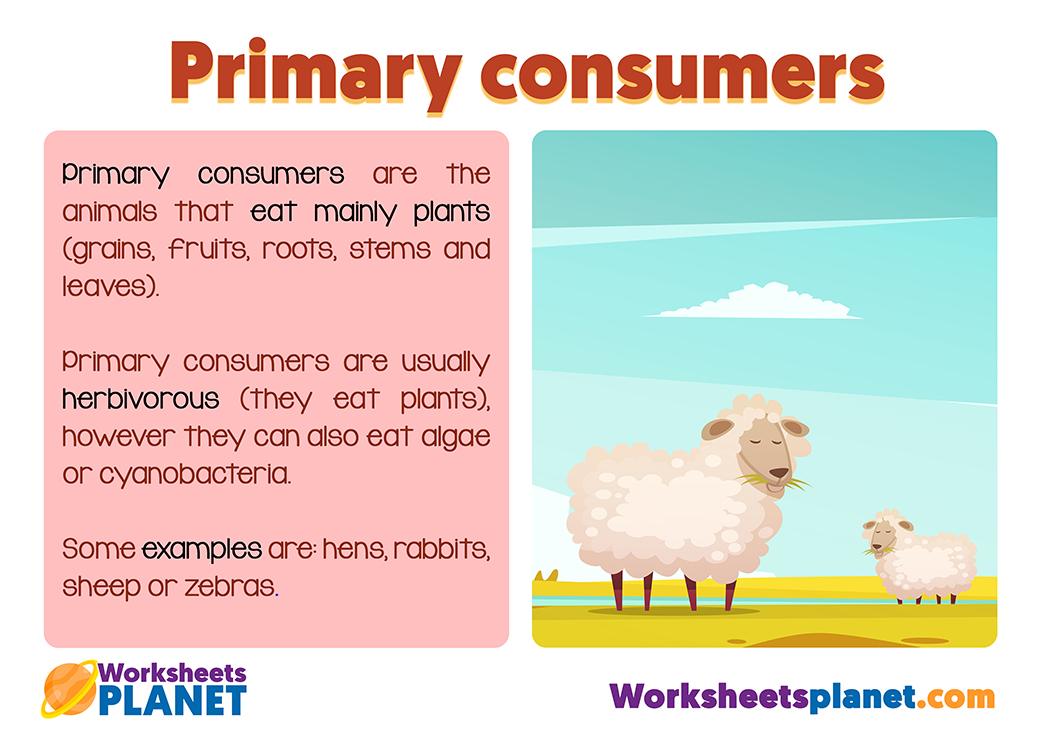
- Primary consumers: They are the animals that eat mainly plants (grains, fruits, roots, stems and leaves). Primary consumers are usually herbivorous (they eat plants), however they can also eat algae or cyanobacteria. Some examples are: hens, rabbits, sheep or zebras.
- Secondary consumers: Organisms that eat primary consumers are called secondary consumers. Secondary consumers eat fresh meat they need to hunt theirselves. These animals are carnivorous but they can also be omnivorous. Some examples are: jaguars, foxes, wolves and pumas.
- Tertiary consumers: Organisms that eat secondary consumers are called tertiary consumers. Tertiary consumers are known as hypercarnivorous, what means they eat other carnivorous. For instance: eagles eat snakes and hyenas eat carrion. Some examples are: sharks, killer whales, tigers or seals.
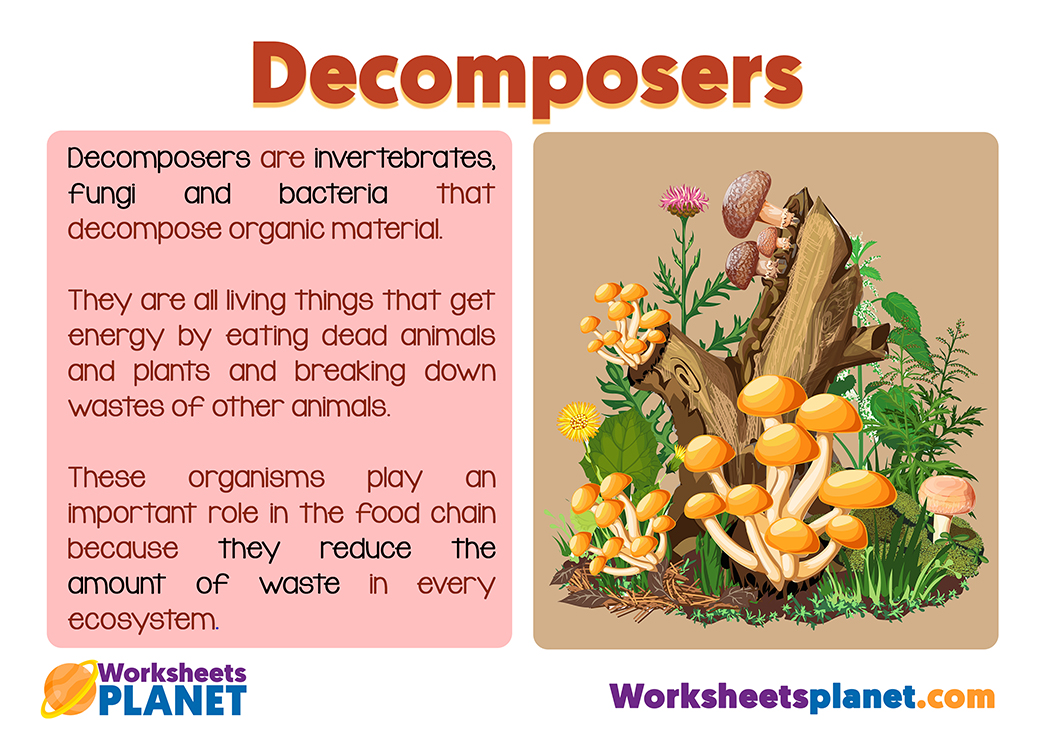
What are the decomposers in the food chain?
Decomposers are invertebrates, fungi and bacteria that decompose organic material. They are all living things that get energy by eating dead animals and plants and breaking down wastes of other animals. These organisms play an important role in the food chain because they reduce the amount of waste in every ecosystem.
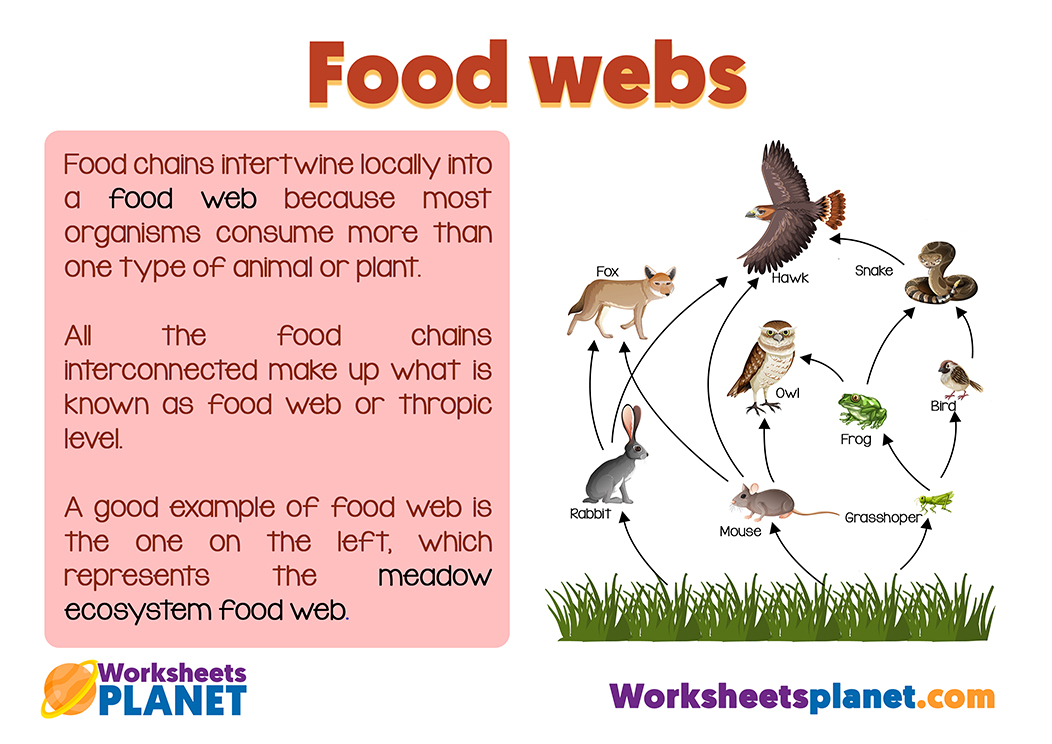
What is a food web?
Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. All the food chains interconnected make up what is known as food web or thropic level. A good example of food web is the one on the left, which represents the meadow ecosystem food web.